Batch methods
Batch methods can generate all the experimental trials before conducting any experiments. See the following.
Simple Strategies
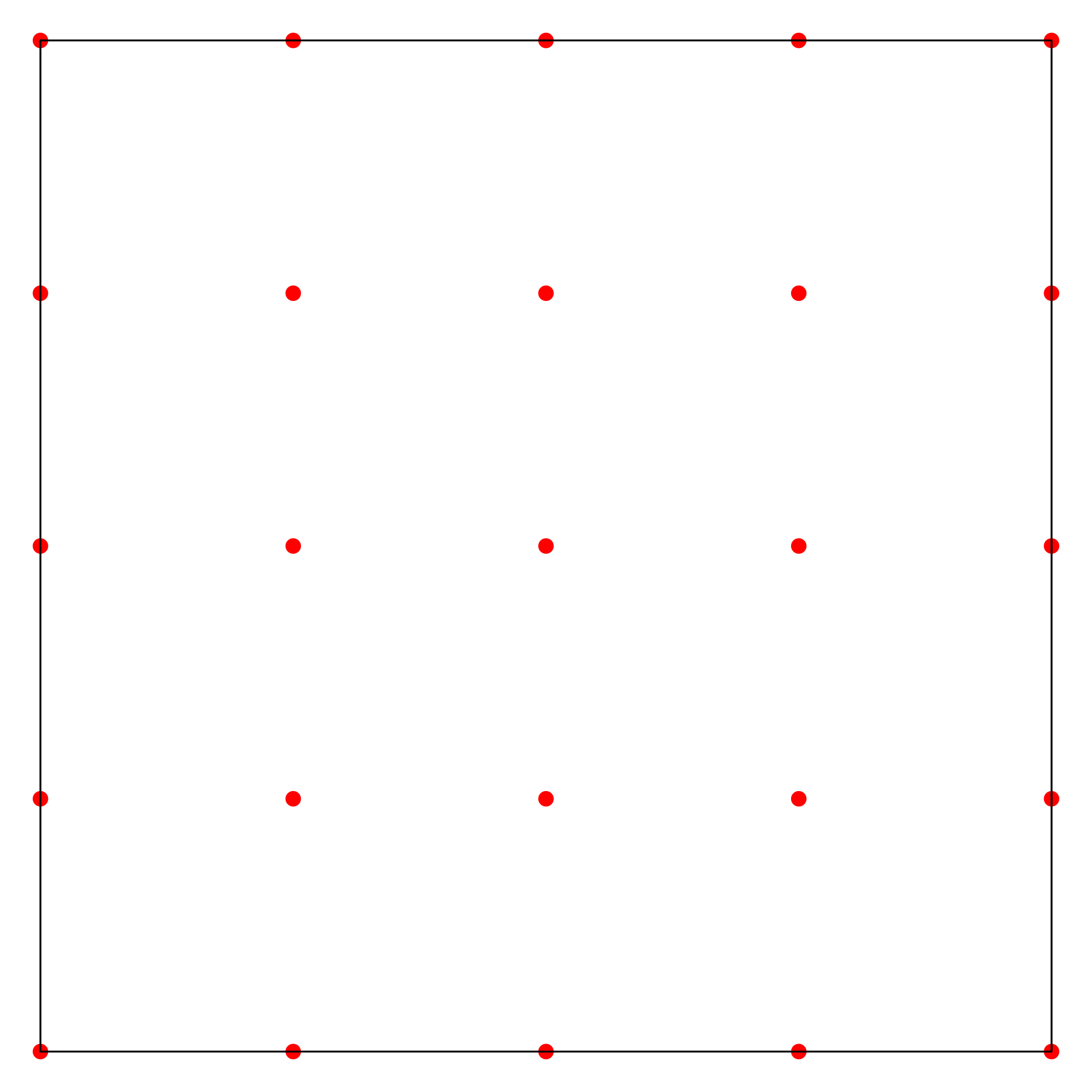
Grid Search (Grid): exhaustive search over grid combinations.
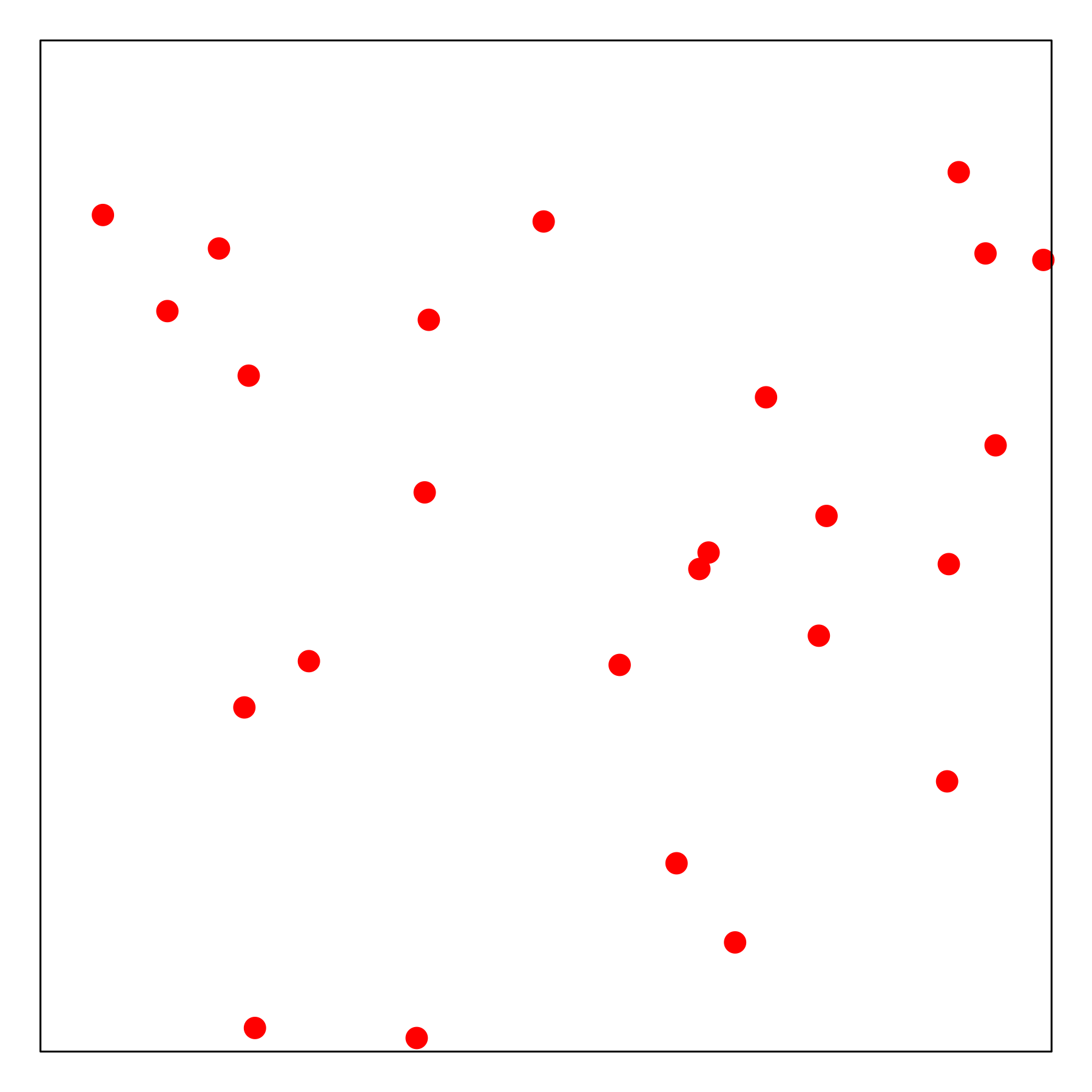
Random Search (Rand): it is more flexible than grid search, when not all hyperparameters are equally important. Furthermore, new trials can be added without adjustment and the experiments can also be stopped any time ([Bergstra2012]).
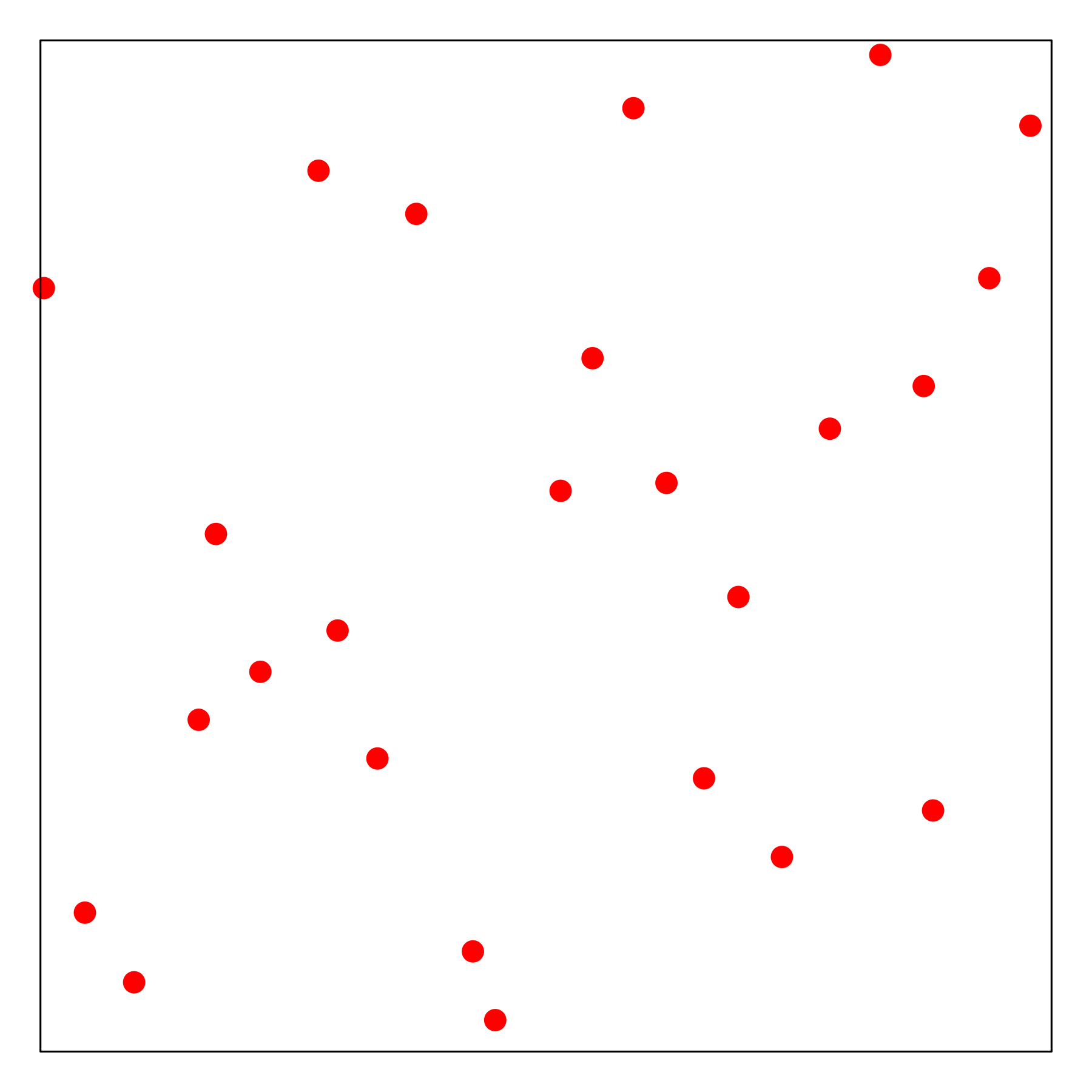
Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS): near-random sample ([McKay1978]).
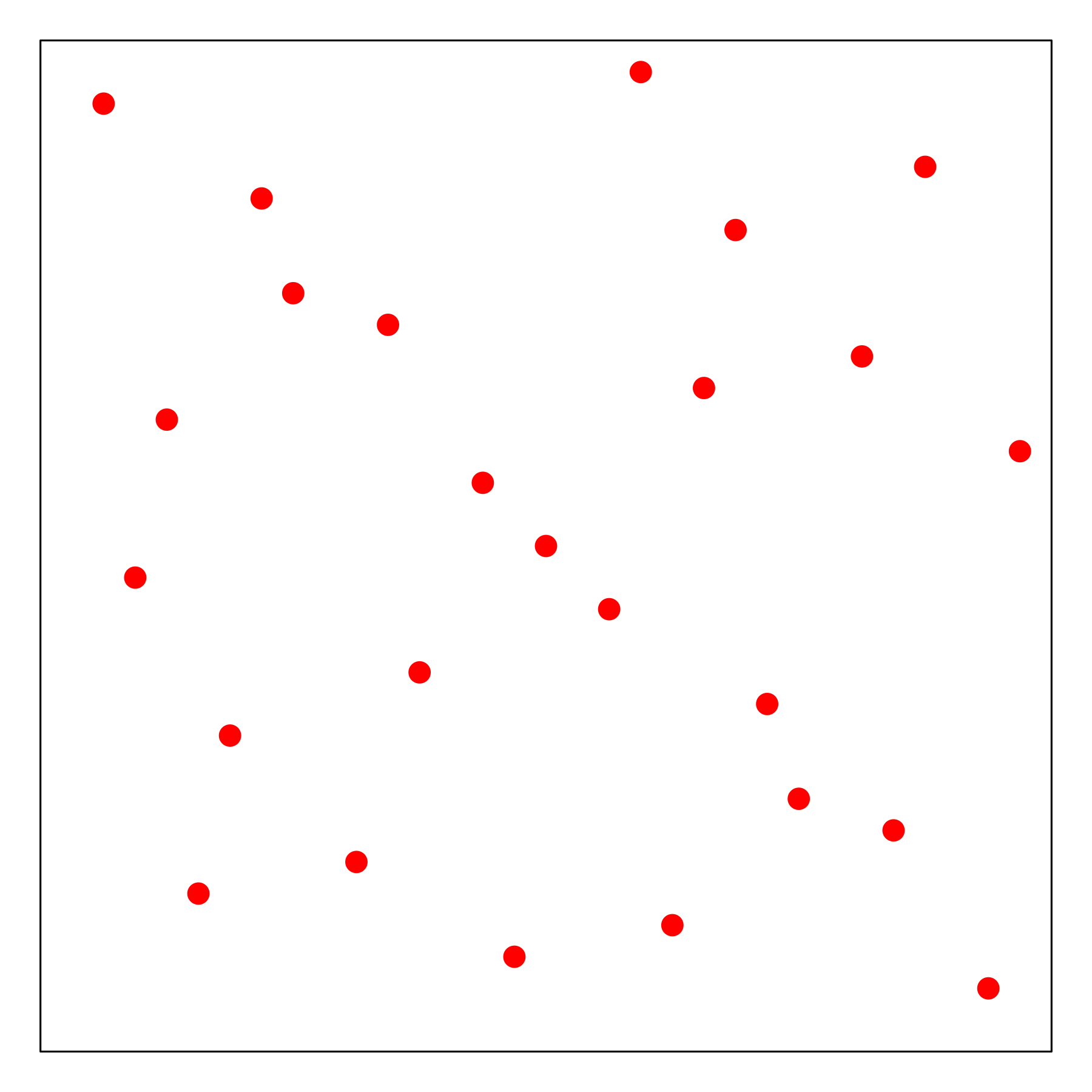
Sobol Sequence (Sobol): quasi-random low-discrepancy sequence ([Sobol967]).
The figures below present the demo sampling history of the four mentioned approaches, including Grid search (top left), Random search (top right), Latin hypercube (bottom left) and Sobol Sequence (bottom right).
Pros and Cons
Easy to be paralleled, trials can be generated without too much burden.
The information of existing experiments is not utilized, which is not efficient.
To select an appropriate number of design points is always difficult, with potential over-sampling and under-sampling problems.
Example Usage
Grid Search:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sequd import GridSearch
iris = datasets.load_iris()
ParaSpace = {'C':{'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-6, 16], 'Wrapper': np.exp2},
'gamma': {'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-16, 6], 'Wrapper': np.exp2}}
estimator = svm.SVC()
cv = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=1, shuffle=True)
clf = GridSearch(ParaSpace, max_runs=100, n_jobs=10,
estimator=estimator, cv=cv, refit=True, verbose=True)
clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
clf.plot_scores()
Random Search:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sequd import RandSearch
iris = datasets.load_iris()
ParaSpace = {'C':{'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-6, 16], 'Wrapper': np.exp2},
'gamma': {'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-16, 6], 'Wrapper': np.exp2}}
estimator = svm.SVC()
cv = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=1, shuffle=True)
clf = RandSearch(ParaSpace, max_runs=100, n_jobs=10,
estimator=estimator, cv=cv, refit=True, verbose=True)
clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
clf.plot_scores()
Latin Hypercube Sampling:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sequd import LHSSearch
iris = datasets.load_iris()
ParaSpace = {'C':{'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-6, 16], 'Wrapper': np.exp2},
'gamma': {'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-16, 6], 'Wrapper': np.exp2}}
estimator = svm.SVC()
cv = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=1, shuffle=True)
clf = LHSSearch(ParaSpace, max_runs=100, n_jobs=10,
estimator=estimator, cv=cv, refit=True, verbose=True)
clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
clf.plot_scores()
Sobol Sequence:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sequd import SobolSearch
iris = datasets.load_iris()
ParaSpace = {'C':{'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-6, 16], 'Wrapper': np.exp2},
'gamma': {'Type': 'continuous', 'Range': [-16, 6], 'Wrapper': np.exp2}}
estimator = svm.SVC()
cv = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=1, shuffle=True)
clf = SobolSearch(ParaSpace, max_runs=100, n_jobs=10,
estimator=estimator, cv=cv, refit=True, verbose=True)
clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
clf.plot_scores()